Inclinometer section
Inclinometer section
![]()
What is inclinometer monitoring
Inclinometer monitoring is the study of horizontal displacements at different depths. These displacements are detected by instruments called inclinometric probes (mono-biaxial) which detect an inclination inside pipes inserted in the ground (landslides) or inside structures (diaphragms, piles, etc.).
The measurement can take place by means of a manual measurement system (probe + reel + manual datalogger) or by fixed probes and data logger.
The inclinometers section on WMS allows you to graph both manual and automatic inclinometric measurements according to regulatory standards.
The WMS through its panel allows the choice of different types of data processing:
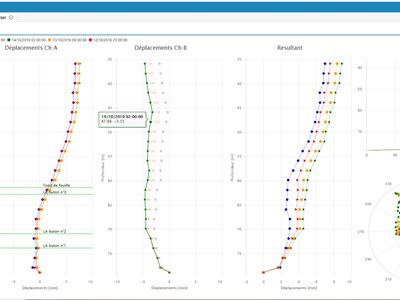
Cumulative shift processing
Cumulative displacements represent the most common representation of inclinometer data and consist of the sum of displacements measured from the base or top of the casing. This processing shows the movement of inclinometers casing starting from the first measurement / probe.
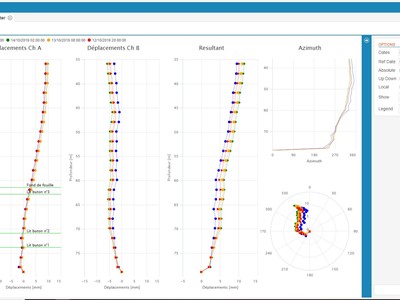
Local displacement processing
The local displacement diagram uses the data from the mean deviation and compares it with the data from the zero reading. This diagram reveals the exact depth where the displacements are taking place. It has the advantage of avoiding cumulative errors along the vertical.
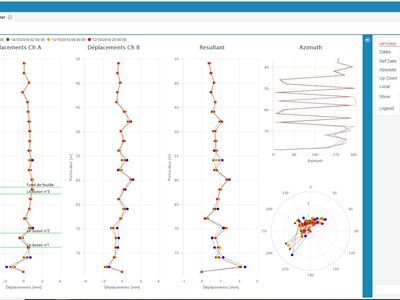
Absolute displacement processing
The absolute displacement diagram reveals the geometry of the inclinometer casing immediately after installation. Although this diagram does not show displacements, it can demonstrate the points where the non-verticality of the pipe can cause errors.
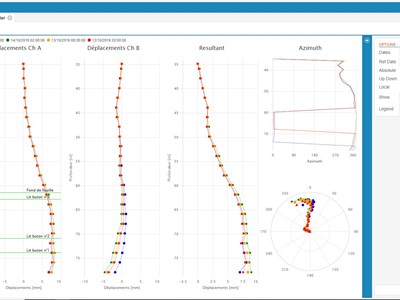
Furthermore, the WMS is able to switch from the display of the displacements along the main axes of the casing (A / B) to different reference systems (e.g. North / East).